How to Detect a Drupal Installation
On 15th October Drupal project disclosed a severely critical vulnerability SA-CORE-2014-005 in Drupal core. Durpal is one of the most commonly used Content Management System (CMS), apart from Wordpress and Joomla. CMS helps in organizing and storing files of a website.
The vulnerability affects Drupal version 7.x, before 7.32, and some deployments of 6.x. An SQL injection vulnerability is present in Drupal’s abstraction API layer and an unauthenticated user can easily exploit it. More details about the vulnerability are available at PSA-2014-003.
Lets look into some signatures which can be used to detect a Drupal installation:
-
CHANGELOG.txt: A default Drupal installation will have a CHANGELOG.txt file present in the root folder of the website. The presence of this file helps in couple of ways, firstly, it affirms presence of Drupal CMS and secondly helps in extracting the version of the Drupal running on the website. One can check Drupal’s website to check how does this work.
-
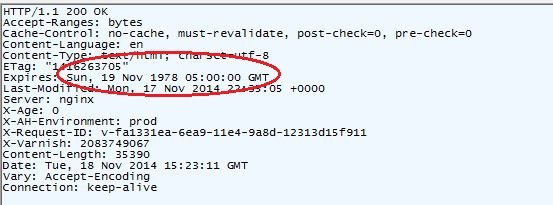
HTTP Expire header: A default Drupal installation have value of ‘Sun, 19 Nov 1978 05:00:00 GMT’ for expires header. It is fairly a good signature as not many servers will keep exactly this value.
-
X-Generator HTTP Header: A default installation also sends a ‘X-Generator’ header in the HTTP response with value ‘Drupal 7 (http://drupal.org)’ .
-
Looking for Drupal modules: In case above mentioned methods are disabled by the server admin (which is very likely), one can scan for Drupal specific plugins. An exhaustive list is available here.
Determining Version
Above methods, apart from CHANGELOG.txt, can only give us only a yes/no. But if one need to go a bit further and wants to determine the version of Drupal running??
To solve this problem, one can use the fact that Drupal is an open source tool. Clone the Drupal code and look for the file which is most changed across various versions. One would prefer to look for javascript or css files, as these will be easy to fetch and unlikely to be changed by the website developer. In my short research I found using modules/color/color.js is a nice place to start with. Generate a SHA-1 hash of color.js across various versions of Drupal, then fetch this file from the website and hash and check against an already generated hash table to determine the version, or at least a range. You can practice this technique here.
Will update this post in case I find some more signatures. If you know one and would like to share, please leave it in the comments below.
Keep hacking !! :D