SSL/TLS Session Establishment
In the previous article I talked about introductory facts of SSL/TLS. In this post I will be looking at how a TLS session is established and introduction to internals of TLS protocol.Further in this post it is assumed that TCP is the underlying transport protocol on top of which TLS is working.
TLS consists of two protocols, TLS Handshake Protocol and TLS Record Protocol and can be depicted as in the image below.
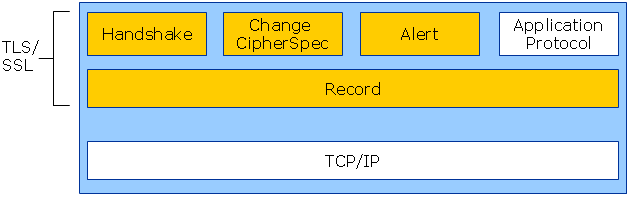
From RFC 5246, the TLS Record Protocol is used for encapsulation of various higher-level protocols. One such encapsulated protocol, the TLS Handshake Protocol, allows the server and client to authenticate each other and to negotiate an encryption and cryptographic keys before the application protocol transmits or receives its first byte of data. The TLS Handshake Protocol provides connection security that has three basic properties:
- The peer’s identity can be authenticated using asymmetric cryptography ( RSA, DSA etc).
- The negotiation of a shared secret is secure.
- The negotiation is reliable.
When a TLS session is established, it could be resumption of a previous session between client and server or totally a new session. Firstly, let us see how a new session is established and then how session resumption works.
TLS new session negotiation
Post TCP 3-way handshake, TLS session establishment initiates. This can be observed in the wireshark snapshot below.
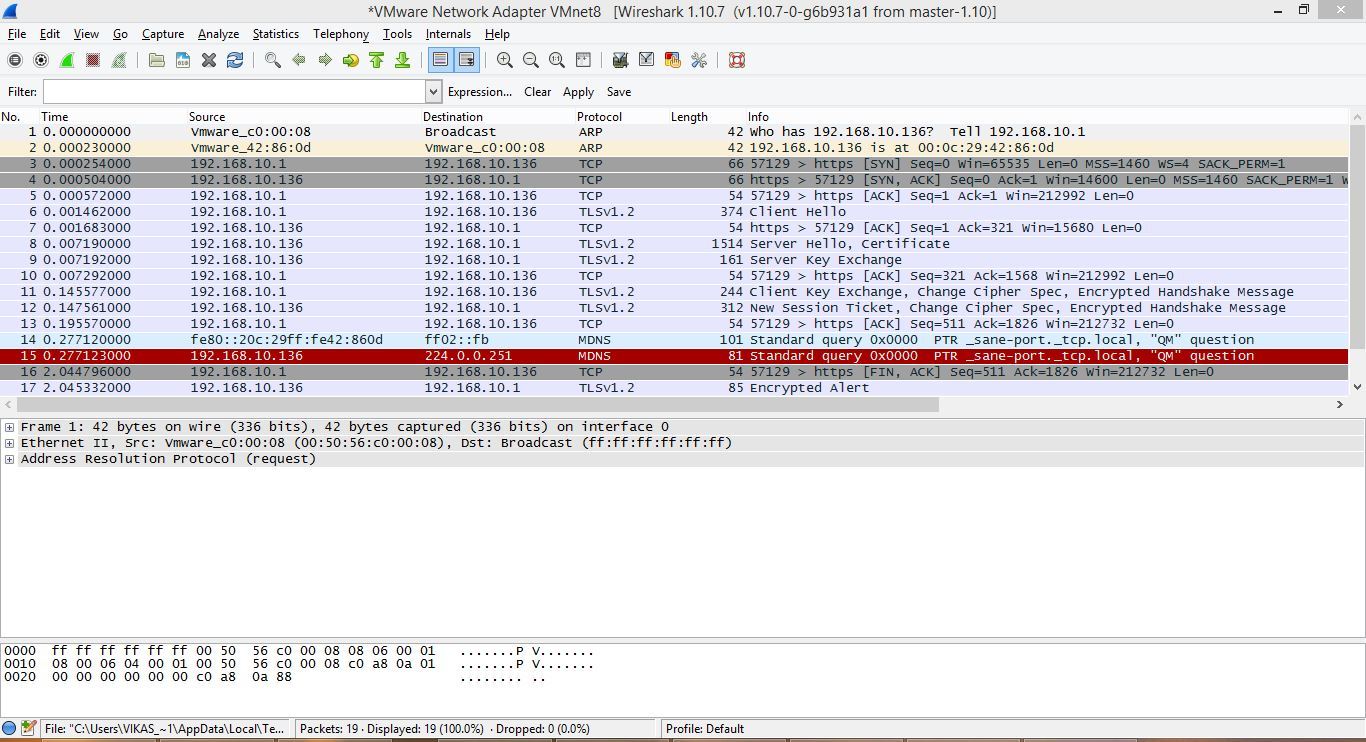
The client starts the initiation process by sending a Client Hello packet. Client Hello contains vital information like max TLS version supported by the client, cipher suits supported, compression algorithms supported and various TLS extensions supported by the client. Heartbeat is a commonly used extension and Heartbleed bug was present in this TLS extension in OpenSSL library.
On receiving Client Hello, server responds by sending a Server Hello message. Server Hello message contains parameters on which the two ends are agreeing to communicate. These parameters include, TLS version, a cipher suit (chosen from the cipher suits advertised by the client), compression algorithm and TLS extensions which will be used by the two peers. In case the TLS session is being negotiated for the first time, Server Hello may return a Session ID, which can be used in future for session resumption. If Session ID is empty, it implies that server is not willing to resume session in future. In case server does not support any of the cipher suits advertised by client, then a TLS Alert message is sent by the server instead of Server Hello.
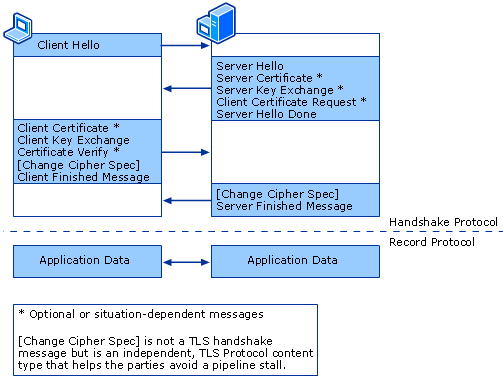
The alert sub-protocol is a component of the Handshake protocol that includes event-driven alert messages that can be sent from either party. Following an alert message the session is either ended or the recipient is given the choice of whether or not to end the session. The alerts are defined in the TLS specification in RFC 2246.
In Server Certificate message, server sends a certificate to the client. This certificate is used for authentication of the server and also contains the server’s public key. The public key is used to encrypt the pre-master secret. If the name of the server in the certificate does not match the URL used by the client to connect, then in most of the popular modern browser a warning message is generated.
Server Key Exchange message is optional. It is used to send a temporary key to the client, which will be used for pre-master secret encryption. It is used in the situation like the server certificate does not contain the server’s public key.
Client Certificate Request message is also an optional one and used when server requests the client to provide a certificate to authenticate client.
Server Hello Done message is used by the server to indicate that communication from server is finished and now it is awaiting further response from the client.
Client Response to Server
Client Certificate message is optional and only sent if server has requested for a client certificate. Client certificate contains client’s public key.
Client Key Exchange message is sent after computing the pre-master secret using the two random values sent by client and server respectively in their hello messages. The pre-master secret is encrypted using server’s public key. If the server is able to decrypt it, then client is assured that the server has the correct private key. It is the most important step in the whole process to establish the authenticity of the server and continue further with protocol negotiation. Message also include protocol version to match against the version sent originally in the Client Hello. This is important to prevent protocol version rollback attacks.
Certificate Verify message is sent only if Client Certificate message was sent previously. This message comprises of hashes of all the messages up till now, encrypted by client’s private key.
Change Cipher Spec (CCS) message notifies the server that all the messages after Client Finished
Client Finished message consists of hash of all the conversation to further ensure the authenticity of the client. This is the first message that the record layer encrypts and hashes.
Server Final Response to Client
Change Cipher Spec message, similar to client’s CCS message, is used by server to notify that from here on server will begin encrypting the messages.
Server Finished message consists of hash of the entire exchange till now using session key and MAC secret. If the client and decrypt and validate the hash, then the TLS handshake process was successful and the keys computed locally at client and server match and are correct.
TLS Session Resumption
Above we looked into how a new TLS session is established. But establishing a new TLS session is a very CPU intensive and time consuming process. It requires two round trips for a full handshake to complete. If the client and server can cache the Session IDs exchanged between them, it can be used to resume the previous TLS session. In simple words, if the client and server remember the previously negotiated parameters then the communication can be carried on with those parameters itself. To resume a session with a given Session ID is called as abbreviated handshake, described in RFC 5077. This short handshake is depicted in the flow diagram below.
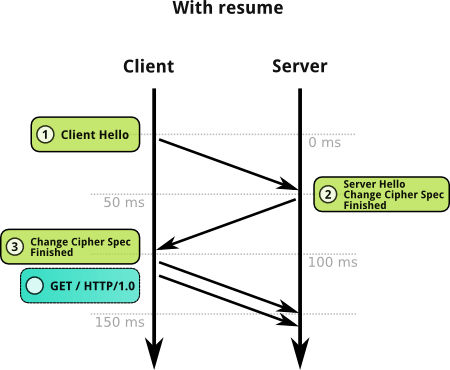
Some additional information, CVE-2014-0224 or the CCS Injection attack involves sending the client CCS packet before the master secret is calculated. By doing so, the master secret is based on a weak pre-master secret and hence easily guessable. You can read more about it here.
Thats all for this post, in the next one I will break down Client Hello message and see how the various TLS sub-protocol work.